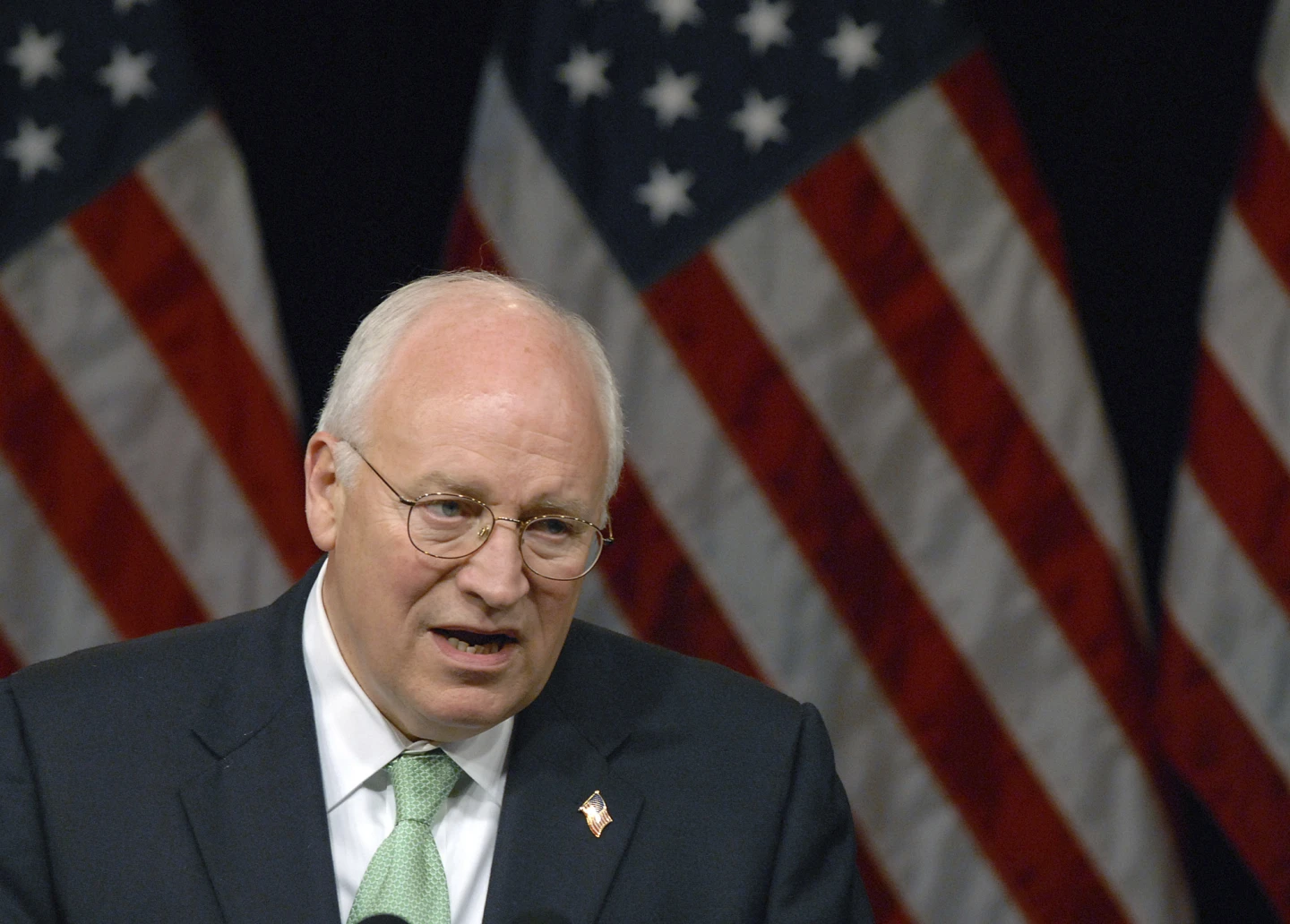
Dick Cheney, former Vice President of the United States, died at the age of 84, leaving behind a legacy marked by both admiration and controversy. Known for his policy decisions during the presidency of George W. Bush, Cheney played a vital role as an architect of the 'War on Terror' following the events of September 11, 2001. His influence extended beyond military actions; he actively shaped domestic policies and held significant power within Washington.
Born in Lincoln, Nebraska, in 1941, Cheney navigated through various political roles from the 1970s onward, including serving as White House Chief of Staff and Defense Secretary during pivotal moments in U.S. history. His tenure at the Department of Defense was notable for managing the military during the first Gulf War, demonstrating characteristics of a hawkish leader who supported substantial military oversight and intervention.
In the years following his vice presidency, Cheney's criticisms of the Republican party and support for issues such as marriage equality for his daughter, who is a lesbian, revealed a personal evolution that contrasted starkly with his earlier conservative stances. This contradiction left many to grapple with his legacy, weighing the commendable against the condemnable.
Ultimately, Cheney will be remembered as a divisive figure, celebrating his achievements while critiquing his decisions that have shaped contemporary debates over American foreign policy, personal liberties, and ideological purity within the Republican party.
Born in Lincoln, Nebraska, in 1941, Cheney navigated through various political roles from the 1970s onward, including serving as White House Chief of Staff and Defense Secretary during pivotal moments in U.S. history. His tenure at the Department of Defense was notable for managing the military during the first Gulf War, demonstrating characteristics of a hawkish leader who supported substantial military oversight and intervention.
In the years following his vice presidency, Cheney's criticisms of the Republican party and support for issues such as marriage equality for his daughter, who is a lesbian, revealed a personal evolution that contrasted starkly with his earlier conservative stances. This contradiction left many to grapple with his legacy, weighing the commendable against the condemnable.
Ultimately, Cheney will be remembered as a divisive figure, celebrating his achievements while critiquing his decisions that have shaped contemporary debates over American foreign policy, personal liberties, and ideological purity within the Republican party.