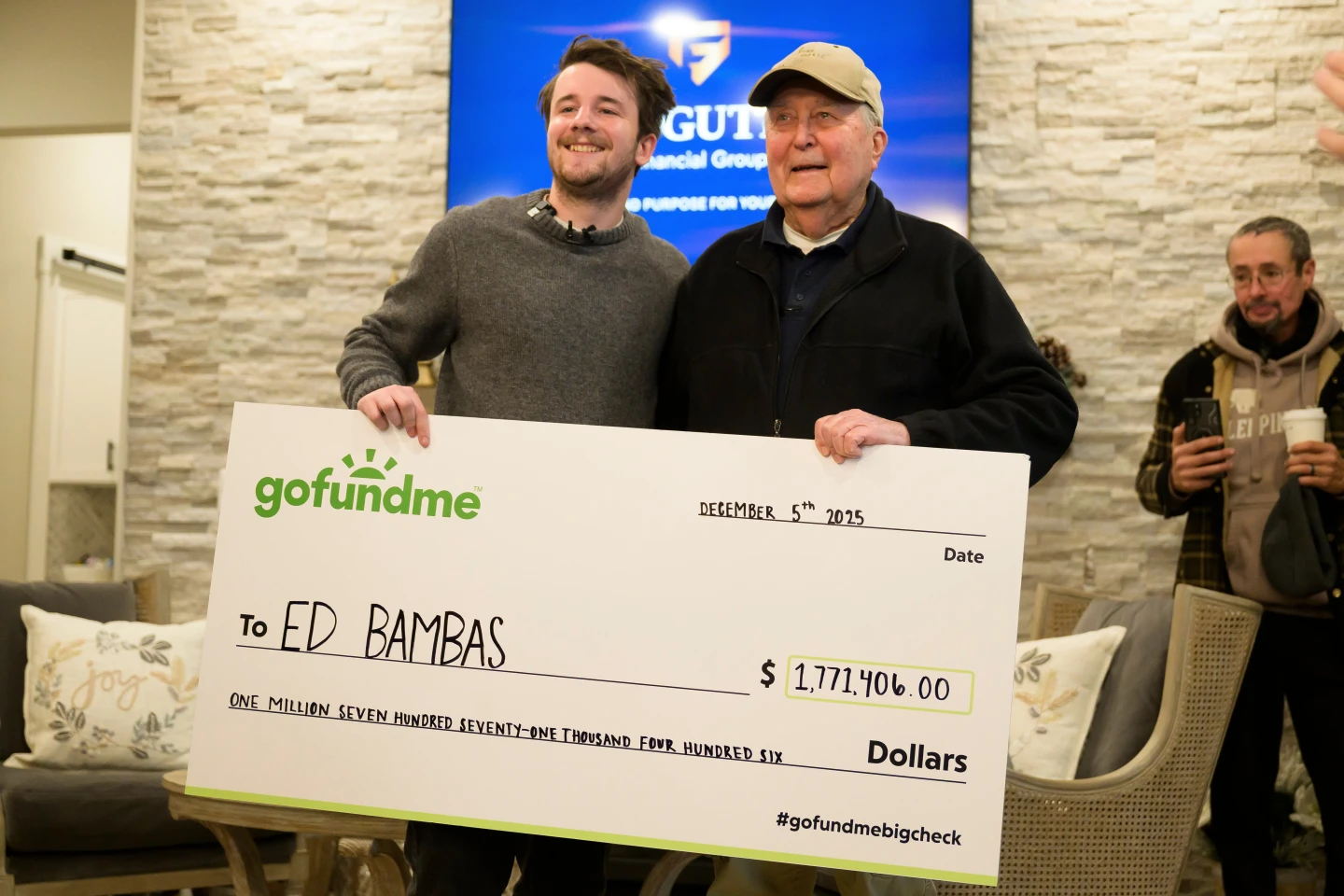
In the face of escalating healthcare expenses and economic challenges, crowdfunding has become an essential tool for many seeking financial support from their communities. Quintin Sharpe, a 27-year-old wealth manager from Wisconsin, recognizes the ethical imperatives involved in supporting community members. His experiences, particularly with crowdfunding for a classmate's family struck by tragedy, highlight both the speed and the complexities of modern philanthropy.
According to a recent AP-NORC poll, nearly 20% of U.S. adults donated to a crowdfunding campaign last year, primarily to assist with medical costs. Sharpe notes that the streamlined nature of crowdfunding platforms like GoFundMe often allows for immediate assistance without the bureaucratic delays associated with traditional charitable giving.
However, this expansion in charitable sectors is accompanied by skepticism. Many Americans express doubts about whether funds raised through these platforms are used responsibly and whether the campaigns accurately reflect the needs of those involved. These sentiments were echoed by Sharpe himself, who believes that each campaign's trustworthiness ultimately hinges on the intent of the recipient.
Generally, donations to crowdfunding campaigns tend to be modest. Six out of ten donors typically contribute $50 or less, reflecting a reliance on robust personal networks rather than large-scale fundraising efforts. Karla Galdamez from California explains how word-of-mouth has revived crowdfunding campaigns among her group of educators, particularly during difficult times.
Moreover, medical crowdfunding has become increasingly commonplace, with advocates suggesting that fundraising could help avert debilitating debt stemming from unforeseen health crises. The poll indicated that approximately 40% of donors specifically cited medical expenses as their primary motive for contributing, revealing the alarming intersection of healthcare inadequacy and economic vulnerability.
Despite the convenience, doubts about reasonable service fees charged by crowdfunding platforms persist. Only a minority of people express confidence in the fees' fairness and transparency, with many attributing their reluctance to past experiences of heightened costs associated with online fundraising.
Ultimately, while crowdfunding presents a modern avenue for raising essential funds, significant barriers still exist. Alarming data reflects the crisis many face, forcing them to resort to crowdsourcing rather than relying on systemic support, raising questions about the efficacy and ethics of fundraising models in upholding human dignity in a society where health and stability often feel precarious.